Understanding LC Discounting
LC discounting, also known as Letter of Credit discounting, is a financial arrangement in which a beneficiary (typically an exporter) receives early payment for their goods or services by selling their rights to receive funds from a Letter of Credit (LC) to a bank or financial institution. This practice is commonly used in international trade to improve cash flow and reduce the payment cycle.
Here's how LC discounting works in India:
-
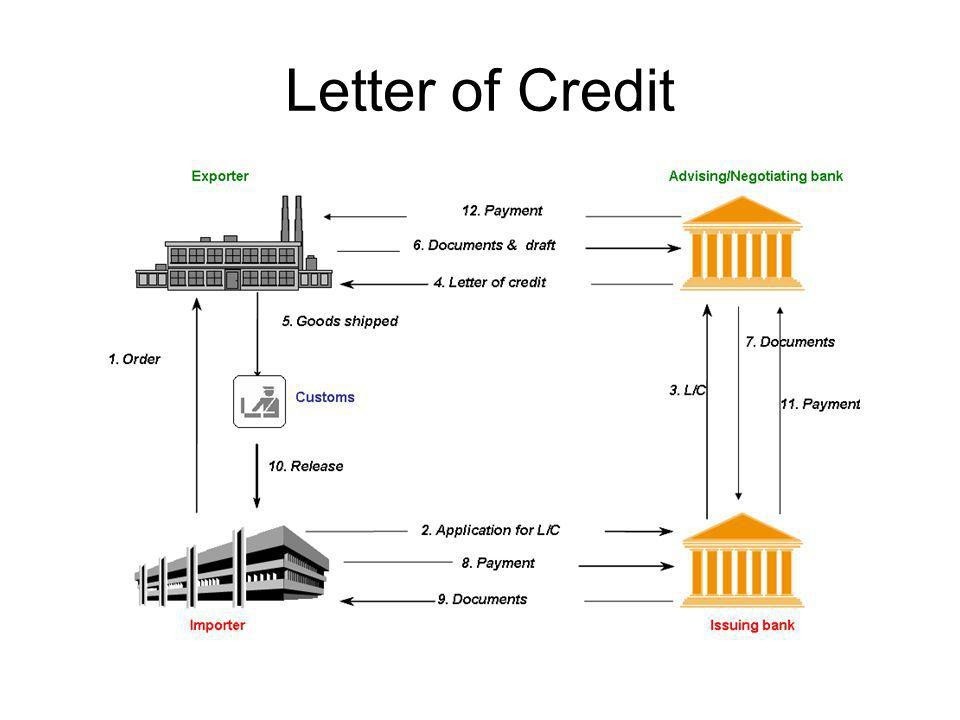
Initiation of Letter of Credit: The importer (buyer) and exporter (seller) agree on the terms of the trade transaction, including the use of an LC as a payment method. The importer's bank (issuing bank) issues the LC in favor of the exporter (beneficiary), specifying the payment conditions and documents required for payment.
-
Presentation of Documents: The exporter ships the goods or provides the agreed-upon services and prepares the necessary shipping and financial documents as per the LC's terms. These documents typically include the invoice, bill of lading, packing list, and certificate of origin.
-
Discounting Request: Instead of waiting for the LC to mature and the importer's bank to release payment, the exporter may choose to discount the LC. To do this, the exporter approaches their own bank or a financial institution and requests LC discounting.
-
Bank Assessment: The bank or financial institution reviews the LC and the accompanying documents to ensure they comply with the terms and conditions. If everything is in order, the bank may agree to discount the LC.
-
Discounting Agreement: The bank and the exporter enter into a discounting agreement, wherein the bank agrees to pay the exporter the discounted value of the LC. The discount amount is calculated based on factors such as the LC's face value, the prevailing interest rate, and the number of days remaining until the LC matures.
-
Payment to Exporter: Upon reaching an agreement, the bank provides immediate payment to the exporter for the discounted amount. This allows the exporter to access funds sooner, improving their cash flow and liquidity.
-
Bank's Role: The bank then takes possession of the LC and associated documents. When the LC matures, the bank presents the documents to the importer's bank for payment, as per the LC's terms.
-
Settlement: When the importer's bank pays the face value of the LC upon presentation of compliant documents, the bank that discounted the LC recovers the discounted amount it paid to the exporter. The difference between the face value and the discounted amount is the bank's profit or fee for providing the discounting service.
LC discounting offers several advantages to exporters in India:
-
Improved Cash Flow: Exporters can access funds earlier than they would if they waited for the LC to mature, allowing them to cover operating expenses and invest in new business opportunities.
-
Reduced Credit Risk: By discounting the LC, exporters transfer the credit risk associated with the importer's bank to the discounting bank. This can mitigate the risk of non-payment.
-
Flexibility: Exporters have greater control over their cash flow and can better manage their working capital needs.
-
Access to Finance: LC discounting provides exporters with a source of financing that is directly tied to their trade transactions.
It's important to note that LC discounting involves fees and interest charges, and the exact terms and costs can vary between banks and financial institutions.
